As a seller using Amazon FBA, you must calculate your profitability, both before and after launching. When conducting Amazon product research, you must estimate your product’s potential before launching, considering your Amazon FBA costs, investments costs, and the estimated sales. After choosing the right product to sell, you must stay abreast of fees and outgoing to ensure your business’s continuity.
However, unfortunately, several Amazon sellers lose their money because they do not know how to calculate Amazon FBA profit margin and costs. This guide illustrates the step-by-step ways to calculate your profit margin and costs so you can price your products correctly.
Let us get straight into it!
First, what types of Amazon margin will you encounter?
Technically, there are two main types of Amazon profit margin: operating profit margins and gross profit margins.
The operating profit margin (net margin) refers to the money spent to get your business running again after sales. This includes expenses and fees. Although somewhat similar, gross margin refers to the total fees from the beginning till the end.
As an Amazon FBA seller, below are the fees you will most likely encounter:
- Referral Fee: This is the percentage charge on every sale you make on Amazon. It is usually a percentage of the price of your product.
- Seller account fee: This is the money paid to Amazon monthly to own a seller account.
- FBA: You have to pay Amazon to use FBA and enjoy the numerous benefits attached. This fee includes the fulfilment per unit fee, inventory storage fee, etc.
- Variable Closing Fee: Amazon deducts the shipping cost of an item.
Having understood the main types of profit margins on Amazon, including the fundamental fees attached, let us deep-dive into the ways you can accurately calculate Amazon FBA profit margin!
How to Calculate Amazon FBA Margin
As mentioned above, there are two types of Amazon profit margin: Net margin and gross margin. While the Net margin includes the business profitability, gross margin is a measure of a product’s profitability.
We have also taken an intentional swipe at the advantages of calculating the Amazon profit margin in the introductory section of this article. However, the big question is, how do you know if your calculations are accurate? Before you start to calculate your profit margin, you should be conscious of the following:
Be long-term oriented
The short-term approach to selling on Amazon isn’t sustainable. Temporarily lowering your margins to increase sales and scale your business is a better approach to making higher long-term profits. It is unwise to underestimate the potency of patience and consistency.
2. Each business is unique.
“Good” profit margins are relative, varying across industries, business goals, and business sizes. In essence, what works for other Amazon sellers might not work for you, especially if you aren’t venturing into the same niche. Hence, you must be intentional about your decisions, conducting the proper research before making a choice or creating a strategy.
3. Consider Amazon FBA Fees
Most sellers fail to include Amazon fees in their calculations. When calculating, ensure you include the fees described above: Seller account fee, referral fee, storage fees, fulfilment fee, etc.
4. The 3X rule
The 3x rule is an excellent means of pricing your products, especially for beginners. This rule infers making the price of your product 3x its cost. For instance, if your product costs $2, sell it for $6. Each dollar caters for any of the three outcomes below:
- Cost
- Fee
- 100% return of investment
However, the 3x rule is somewhat limiting. The experts at Zon Hack advise Amazon FBA sellers to implement the Profit Margin Formular illustrated below when to calculate their profit margins.
The Profit Margin Formula
As mentioned earlier, the gross profit margin is a measure of your product’s profitability. Below is the formula for its calculation:
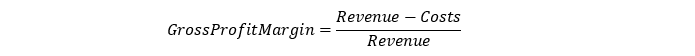
To calculate the profit margin earned from the sales of your product, first determine the total costs and revenue for the product; after that, insert them into the formula illustrated above.
How to Increase Your Profit Margin on Amazon
1. Use repricing software.
Most successful Amazon sellers typically use this as their topmost strategy when seeking to increase their Amazon profit margin, largely because it is easy and relatively direct.
The rapid and ever-constant change in the price of products on Amazon may make it somewhat difficult for you to stay up-to-date. Hence, instead of repricing your product manually, you can make use of repricing software. Speak with any of the experts at Zon Hack today to find the best way to go about it!
2. Group products together
Bundling products offer plenty of importance and less risk, especially in terms of profits. It’s closely related to offering discounts on your products. Buyers (humans, generally) enjoy freebies, getting deals that help them save their money. They prefer to buy bundled products at a less high price than buying the products individually. This is beneficial to you as an Amazon seller, too. It translates to an increase in sales volume and, in turn, increased profit margin.
However, while bundling your products, ensure that you create a new listing for each bundle.
3. Use credit cards for inventory purchases.
While it may appear cool to pay your suppliers with a third-party agent such as PayPal, you may want to reconsider such actions, especially as you scale your business higher.
Using a credit card instead of PayPal for your inventory purchases is an excellent way to replenish you’re your inventory. It helps you to return more money to your wallet through points, cashback, and a few other rewards. Just ensure you pay your balance monthly; otherwise, you may be risking the nullification of your earned increased profit.
4. Buy your supplier out.
Whenever your supplier has just a few product units remaining, you can take such advantage to buy the rest out, especially if your supplier doesn’t deal with many Amazon sellers.
This is somewhat related to forcing a market monopoly. In essence, while your competitors are waiting for the delivery of their purchases, you will still have plenty of units in your inventory to sell. This makes you the sole seller for some time, making you earn as much as possible during that period.
5. Monitor the changing prices of your suppliers
Invest some time in monitoring your supplier’s changing costs: when the price increases and decreases. However, this largely depends on how big your supplier is. While some supplier’s catalogue might be relatively small, some of them have hundreds or thousands of items in their catalogue. This may be time-consuming and quite tasking.
So, instead of reviewing the products individually, it is advisable to automate the process. You can monitor your supplier’s changing prices by using a profit analyzer. Remember that you are on the lookout for a drop in price in other to buy such products in bulk and sell them on Amazon for increased profit margins.
6. Take advantage of out-of-stock products.
Have you noticed any out-of-stock items with a high search volume? It is advisable to capitalize on such products. It is simply helping buyers to find what they are seeking but no longer available on Amazon. It is also very similar to monopolizing the market over a short period.
If you can quickly ship an unavailable item with an excellent sales rank to an Amazon fulfilment centre, you can be sure of enjoying buyers’ patronage. Buyers don’t care about who’s providing the product; instead, they just want to have the product without having to wait for a restock.
7. Sell products with high potentials to go out-of-stock
This a highly risky strategy. Nonetheless, if you get your research right before implementing it, you can make huge profits. But then, it is not advisable to make this your main method of increasing your Amazon profit margin.
This strategy entails searching for items with a good sales rank but often becomes out-of-stock. Purchase such products, wait for other listings to run out of the product, then activate your listing. This time, you would be selling at a relatively higher price. Buyers will have no other option but to buy, as you seem to be the only option available during that period. They buy, and you have a higher profit margin.
As mentioned above, this method is quite risky because:
- You can’t guarantee that buyers will buy at a higher price. Some buyers may be comfortable with waiting for lower-priced alternatives.
- You may overprice your products unknowingly.
- You risk your storage fee cancelling or exceeding your profit margin. This happens when it takes a longer time for the product to go out of stock.
- Such a product may go out of demand.
Amazon Seller Costs in 2021
While selling on Amazon can be incredibly profitable, it is essential that you familiarize yourself with the associated fees to have a clearer idea of your total costs and true Amazon profit margin.
Below is a comparatively brief but detailed guide on your fundamental fees as a seller using Amazon FBA.
1. Direct Costs
These are costs incurred when you produce or purchase your products, including the shipping fee of such products.
2. Indirect costs
This includes warehouse costs, insurance, utilities, business travel, bookkeeping, product samples, payroll and benefits, web development, corporate business tax, etc. Basically, Indirect costs are costs incurred when selling your product(s).
3. Amazon fees
Amazon fees include FBA fees, commissions on returned products, FBA inbound shipping fees, sales commissions, returns disposal costs, and return shipping costs. The return shipping costs are charged by both you and your customer.
4. Costs for handling returns after receipt
These costs are incurred when you, as a seller, can’t sell a returned product as a new-conditioned product. They are write-off or write-down costs accompanying the inability to resell your products at the original selling price after such products are returned to you.
The Amazon FBA Calculator
The Amazon FBA calculator is yet another excellent way to accurately calculate your Amazon FBA profit margin and costs.
The Amazon FBA calculator is a useful tool for all FBA sellers. The calculator helps you a great deal to identify the exact amount you will pay in fees to use the FBA (Fulfilment by Amazon) business model, regardless of your product type.
How to use Amazon FBA Calculators
While there are a few types of third-party Amazon FBA calculator, Amazon itself has its traditional model. To use the traditional FBA calculator of Amazon is quite straightforward, with relatively similar methods to other types. Regardless of the country, you are selling from, below are the general steps of using the Amazon FBA calculator:
- Navigate to the product’s page on Amazon.
- Next, enter the product’s cost, shipping costs, and total cost per unit of such a product. To do so, simply switch to the calculator and do as required in the spaces provided.
- Push the “calculate” button and wait for the Amazon FBA calculator to display the detailed breakdown of costs involved with your item.
Conclusion
It has been an interesting journey through this step-by-step guide on how to accurately calculate Amazon FBA profit margins and costs. Knowing the exact steps to take, you can begin making better and informed pricing decisions when pricing your product. While the 3x rule comes in handy for many sellers, do not sideline the long-term approach nor exclude all Amazon seller fees when calculating your profit margin.
Above all, your business belongs to you alone. In essence, you are liable to make the most valuable decision to scale your business. Zon Hack is your go-to guide as an Amazon FBA seller. Right from Amazon product research to help you appropriately price your items, our experts are always available to see you through the entire process.
Knowledge is power: knowing how your products are performing is essential to accurately calculate your Amazon profit margins. The steps explored in this article will help you through the entire process!




