If you’ve ever shopped on Amazon, you’ve probably seen strange strings of numbers and letters embedded in product URLs. These are called ASINs (Amazon Standard Identification Numbers), and they play a crucial role in organizing Amazon’s massive product catalog. Whether you’re a buyer looking for a specific product or a seller trying to optimize your listings, understanding ASINs is key to navigating Amazon’s marketplace.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about ASINs—from what they are and why they matter, to how they work for both buyers and sellers, and the best practices for managing them.
What is an ASIN Number?
An ASIN number is a 10-character alphanumeric code unique to each product on Amazon. It’s used to identify, track, and manage products in Amazon’s catalog, and it’s critical for both customers and sellers. ASINs help improve product searches, inventory tracking, and visibility on the platform.
ASINs are essential for keeping Amazon’s vast product catalog organized. If you’ve ever noticed how easily you can search for a product using its ASIN, this unique number plays a central role in making that process smooth.
Interestingly, Amazon ASINs are marketplace-specific. This means that the ASIN for a product may be different depending on the Amazon site you’re shopping on.
ASIN vs ISBN
Each product on Amazon has its own ASIN—except for books. Books are the only products on Amazon that use ISBNs (International Standard Book Numbers) instead of ASINs. For instance, if you’re browsing for a book, you won’t see a typical 10-character alphanumeric ASIN, but rather a number that follows the ISBN format.
Why ASIN Numbers Are Important?
For Customers
For shoppers, ASINs act as a bridge to a seamless and accurate shopping experience. When you search for a product on Amazon, ASINs ensure that your search returns precise results. This is especially helpful when looking for highly specific items that may not have easily recognizable names or labels.
ASINs also help improve product visibility, ensuring that your search results are populated with relevant products. In fact, if you know the ASIN of a product you want, you can directly enter it into Amazon’s search bar, making the process quicker and more efficient.
For Sellers
For sellers, ASINs are invaluable. They help track inventory, monitor sales, and identify product details quickly. When you list a product on Amazon, you’re assigned a unique ASIN, which becomes essential for managing your product’s performance in the marketplace.
ASINs are also a vital tool for competitor analysis. Sellers often use reverse ASIN lookup tools to gather insights on how their competitors’ products are performing.
ASINs also contribute to ensuring that your product shows up in relevant customer searches. If your product is incorrectly cataloged or listed under the wrong ASIN, it may not appear in the correct search results.
For Amazon
For Amazon, ASINs are the backbone of its vast catalog. They serve as the mechanism by which products are indexed and categorized. Without ASINs, Amazon would have a difficult time organizing and displaying millions of products in a cohesive, easily navigable way.
ASINs are also crucial for search engine optimization (SEO) within Amazon’s own ecosystem. Amazon’s search algorithm indexes products by referencing their ASINs. This ensures that products are displayed in the appropriate search results and helps Amazon prevent duplicate listings.
Furthermore, ASINs help Amazon protect its users from counterfeit products and fraudulent listings. Amazon’s catalog system, built around ASINs, allows the platform to quickly identify and remove any unauthorized or harmful items.
How to Find an ASIN on Amazon?
Now that we understand the significance of ASINs, the next logical question is: How do you find an ASIN for a product?
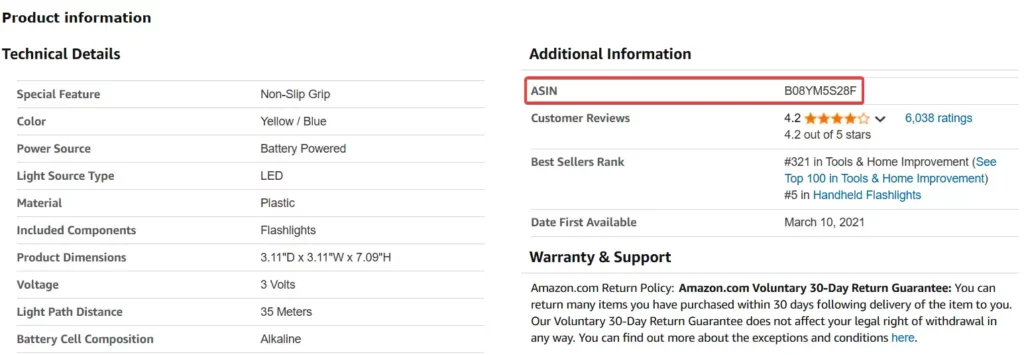
On a Product Page
The easiest way to find an ASIN is by visiting the product page itself. On most product detail pages, you’ll find the ASIN listed in the Product Details or Additional Information section. If you’re using a mobile device, you may need to scroll down a bit to find this information.
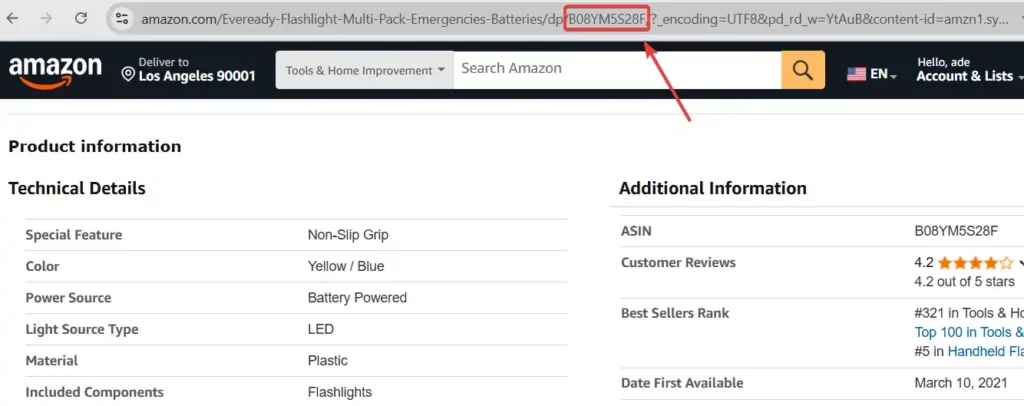
In the URL
You can also find an ASIN embedded directly in the product’s URL. The ASIN typically appears after the /dp/ in the URL structure. For example, in the following URL:
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B08N5WRWNWThe ASIN is B08N5WRWNW. This method is quick and easy, especially if you’re already on a product’s page and need the ASIN for reference.
Using Third-Party Tools
Several third-party tools and extensions can help you retrieve ASINs. Many product research platforms, such as Helium 10, AMZScout, and Jungle Scout, provide ASIN lookup tools that extract ASINs from product pages automatically. These tools are especially useful for sellers doing research on competitors or looking to optimize their own product listings.
Additionally, browser extensions designed for Amazon sellers, like Keepa or CamelCamelCamel, can also help you track product ASINs, monitor pricing trends, and gather historical data on sales rankings.
In Seller Central
For Amazon sellers, Seller Central provides an internal tool to search for ASINs within your own inventory. If you’re trying to find an ASIN for a product you want to sell, you can search by the product name, UPC code, or model number to locate it quickly.
How is an ASIN Assigned?
ASINs are typically auto-generated by Amazon’s system when a new product is listed on the platform. However, sellers can manually add new products to Amazon’s catalog, which in turn generates a new ASIN.
When is a New ASIN Created?
A new ASIN is created when a product is unique and doesn’t already exist in Amazon’s catalog. For instance, if you’re listing a product for the first time, Amazon will assign it a new ASIN based on the details you provide, such as the product’s name, product brand, and identifier (like UPC or EAN).
If you’re selling a product that already exists in Amazon’s catalog, you’re expected to use the existing ASIN for that product. Listing the same product multiple times under different ASINs is considered a violation of Amazon’s policies and can lead to penalties, including the removal of your listings or suspension of your seller account.
Creating a New ASIN: What You Need to Know
Creating a new ASIN is a step every seller must understand, especially if they plan to introduce new products to the market. Amazon has specific guidelines for when and how a new ASIN should be created.
When to Create a New ASIN
You only need to create a new ASIN if the product you’re listing does not already exist in Amazon’s catalog. However, it is essential to ensure the product is genuinely unique. If your product is already available under another ASIN, listing it again as a new product can lead to duplicate listings, which Amazon strictly prohibits.
To create a new ASIN, you’ll need to add a product via Seller Central. During this process, you will be required to provide essential product details like the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number), UPC (Universal Product Code), or EAN (European Article Number). These identifiers help Amazon ensure that the new ASIN is cataloged correctly.
Once the product page is approved, Amazon will assign an ASIN to it, and it will become part of their catalog. The process can take some time, especially if you are submitting a new or unfamiliar product. However, once created, the ASIN will be linked to your listing and visible to potential buyers.
Restrictions on Creating ASINs
Amazon has some restrictions on creating new ASINs. If you are a new seller or do not have sufficient sales history, you may be limited in how many new products you can list. Amazon generally enforces these restrictions to ensure the quality of new listings and to prevent spammy or low-quality products from flooding the marketplace.
It’s also important to note that creating duplicate ASINs is a violation of Amazon’s policies. Each product should only have one ASIN associated with it in Amazon’s catalog. If you try to list a product that is already listed, Amazon will either reject your submission or merge your listing with the existing ASIN.
The Role of Product Identifiers in ASIN Creation
ASINs are often closely tied to product identifiers. These identifiers ensure that products are correctly cataloged and differentiated.
GTIN (Global Trade Item Number)
The GTIN is a globally recognized identifier for products. It’s typically used to create and match ASINs, allowing Amazon to categorize products accurately. GTINs come in several formats, including UPC and EAN, which are the most common types of product identifiers.
UPC (Universal Product Code)
A UPC is a 12-digit code commonly found on retail products in the United States. This code is used to track products in retail environments and is one of the primary identifiers for new ASINs. Sellers are required to provide a UPC when adding a new product to Amazon’s catalog, unless the product falls into a special category (e.g., handmade or custom-made products).
EAN (European Article Number)
The EAN is similar to the UPC but is used primarily in European markets. It can be 12 or 13 digits long, depending on the region. Like the UPC, the EAN helps Amazon organize and identify products in its catalog.
ISBN (International Standard Book Number)
For books, Amazon uses the ISBN instead of an ASIN. The ISBN is a unique identifier for books, ensuring they are cataloged correctly. It is typically 10 or 13 digits long and helps Amazon manage books efficiently across different editions, publishers, and formats.
Reverse ASIN Lookup: A Powerful Tool for Sellers
If you’re an Amazon seller looking to gain an edge over your competition, you’ve probably heard of reverse ASIN lookup. This tool allows sellers to analyze their competitors’ product listings by extracting key information related to their ASINs.
How Reverse ASIN Lookup Works
When you perform a reverse ASIN lookup, you are able to retrieve the keywords that are driving traffic to a product. These are the terms customers are searching for when they find your competitor’s product. Reverse ASIN lookup tools like Keyword Scout can help sellers identify the best keywords to target in their own listings or pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns.
For instance, if you discover that your competitor’s product is ranking for highly relevant keywords, you can adjust your own listings to include those same terms. This technique helps increase your product’s visibility in Amazon search results, improving the chances of a sale.
Benefits for Amazon PPC Campaigns
Reverse ASIN lookup is especially useful for refining your Amazon PPC campaigns. By analyzing which keywords are working for other sellers in your niche, you can optimize your bidding strategy, ensuring you target the most profitable search terms. This method also helps you identify high-converting keywords that are specific to your product category.
ASINs and Brand Protection: Safeguarding Your Listings
For sellers looking to protect their brand and intellectual property, understanding ASINs is crucial. Amazon has various tools and programs in place to help safeguard sellers’ listings and prevent unauthorized or counterfeit products from being listed.
Amazon Brand Registry
Amazon Brand Registry provides sellers with enhanced protection for their ASINs. By enrolling in the Brand Registry, you gain access to tools that help you report intellectual property infringements, including counterfeit goods or unauthorized use of your brand name. This helps ensure that only legitimate sellers can list products under your ASINs.
Brand Gating and Permissions
Amazon has implemented brand gating to restrict unauthorized sellers from listing products under protected ASINs. If you have a registered trademark, Amazon may require permission and invoices to sell products listed under your brand’s ASINs. This helps ensure that your products are only sold by authorized sellers.
Transparency Program
Amazon’s Transparency Program provides an extra layer of protection against counterfeit products. Sellers enrolled in the program receive unique codes that are applied to their products, allowing Amazon to verify their authenticity at each step of the supply chain. This significantly reduces the risk of counterfeit goods being sold under your ASINs.
Merging Duplicate ASINs
Occasionally, duplicate ASINs can be created due to incorrect listings or changes in product details. Amazon allows sellers to merge duplicate ASINs to consolidate product listings and ensure accuracy. Merging ASINs also helps protect trademarks and prevent confusion among buyers who may encounter multiple listings for the same product.
Best Practices for Managing ASINs
Efficient management of ASINs is vital for ensuring that your products appear in the right search results and reach the correct customers. Below are some best practices to keep in mind:
Ensure Accurate ASIN Usage
Always ensure that you are using the correct ASIN for your products. Listing the wrong ASIN can lead to poor search visibility and even listing removals. Always double-check that the ASIN matches the exact product you intend to list.
Avoid Duplicate ASINs
Duplicate ASINs are a major issue on Amazon, as they lead to catalog confusion and harm the customer experience. If you discover that your product has been listed under multiple ASINs, work to consolidate them into one. Always research before creating a new ASIN to ensure the product isn’t already listed.
Regularly Update Product Information
Keeping your product information up-to-date is essential for maintaining the quality of your listings and improving your ranking. Make sure to regularly review your ASINs to ensure that all product details are correct and aligned with Amazon’s guidelines.
Create an ASIN List
Creating a list of your ASINs allows you to keep an overview of all the products you’re selling on Amazon. This can be especially useful when managing a large inventory, as it helps you track each product’s performance and ensure that your listings are optimized.
Additional Information About ASINs
Understanding the finer details of ASINs can provide deeper insight into how Amazon operates. For example, it’s worth noting that:
- ASINs are automatically generated by Amazon’s system when products are listed on the platform.
- Amazon owns all ASINs within its marketplace. Even though sellers create listings, the ASIN itself belongs to Amazon.
- Different regional Amazon websites may use different ASINs for the same product, so be aware if you are selling internationally.
Additionally, while most sellers don’t pay for creating ASINs, high-volume sellers may incur a monthly fee per ASIN if they’re listing a large number of products.

