Amazon’s FBA Capacity Limits dictate the maximum volume of inventory a seller can store at Amazon’s fulfillment centers. This limit, measured in cubic feet, helps sellers plan their inventory while ensuring Amazon’s logistics network operates smoothly. With the 2023 shift to unified monthly limits, sellers now have a more predictable and simplified system. However, effectively navigating these changes requires a deep understanding of the factors influencing capacity and strategies to optimize storage.
What Are FBA Capacity Limits?
FBA Capacity Limits refer to the total allowable inventory volume for sellers using Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) service. This volume is calculated monthly and is based on several factors, including a seller’s Inventory Performance Index (IPI) score, historical sales data, and warehouse capacity. The March 2023 update replaced the older weekly restock and quarterly storage limits, introducing a unified monthly limit to make inventory planning more predictable.
The goal of these limits is twofold: to streamline warehouse operations for Amazon and to empower sellers with greater control over their inventory, enabling them to bid for additional space when needed.
Types of FBA Seller Accounts and Their Capacity Limits
Amazon categorizes sellers based on their account type and selling history, which determines their capacity:
1. Individual Selling Accounts
These accounts have a fixed capacity of 15 cubic feet. Sellers with this type of account cannot increase their limits, making it ideal for small-scale or occasional sellers.
2. New Professional Selling Accounts
Sellers who have been active in FBA for less than 39 weeks are given flexibility without strict capacity limits during this period. This helps new sellers establish a sales history before specific limits are applied.
3. Established Professional Selling Accounts
Amazon determines capacity limits by sellers’ IPI score and sales performance who are active for more than 39 weeks. Higher-performing sellers with good inventory management practices are rewarded with increased capacity.

What Affects FBA Capacity Limits
Several factors come into play when determining a seller’s monthly capacity:
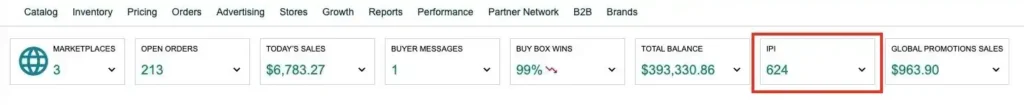
1. Inventory Performance Index (IPI) Score
The IPI score is central to determining FBA capacity. It measures how effectively a seller manages their inventory based on:
- Excess Inventory: Overstocked items that reduce storage efficiency.
- Sell-Through Rate: The speed at which inventory is sold.
- In-Stock Rate: Keeping high-demand items consistently available.
- Stranded Inventory: Products without active listings that occupy valuable storage space.
A high IPI score (above 400) typically leads to higher capacity, while scores below this threshold can result in penalties or lower limits.
2. Historical Sales Volume
Amazon evaluates past sales data to predict future demand and allocate capacity accordingly. Sellers with a strong sales history are generally given priority.
3. Seasonal and Peak Period Adjustments
During peak periods such as Black Friday or holiday seasons, Amazon adjusts limits to accommodate increased demand. Sellers should plan well in advance to avoid storage issues.
4. Fulfillment Center Capacity and Shipment Lead Times
Amazon’s available warehouse space and labor also influence individual capacity limits. Longer shipment lead times may require sellers to reserve capacity earlier to ensure timely restocking.
5. Sales Forecasts and Promotions
Amazon considers sales projections for each ASIN and scheduled promotions. Accurate forecasts are critical for securing sufficient storage space.
6. New Product Launches
Introducing new products affects capacity calculations. Sellers should monitor how their catalog changes impact storage needs.
How to Manage and Increase FBA Capacity Limits
Effective management of FBA capacity is crucial to avoid penalties and optimize sales potential. Here’s how sellers can stay ahead:
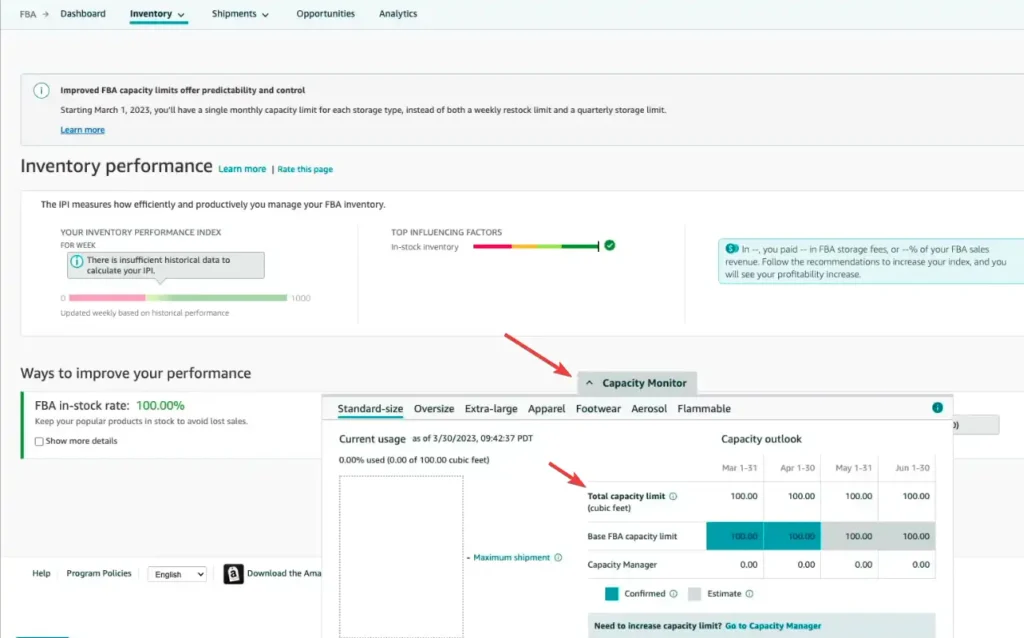
Monitoring Usage
Amazon provides tools like the FBA Capacity Monitor, which allows sellers to track their current storage usage, upcoming limits, and storage breakdowns by category.
Improving IPI Scores
To increase capacity, sellers must maintain a high IPI score. Key steps include:
- Regularly evaluating inventory to minimize excess stock.
- Running promotions to improve sell-through rates.
- Ensuring high-demand products remain in stock.
- Addressing stranded inventory promptly.
Bidding for Additional Capacity
For sellers needing more space, Amazon’s Capacity Manager allows bidding for extra storage. This system involves:
- Specifying the additional volume required.
- Submitting a bid amount as a reservation fee.
- Offsetting fees through performance credits earned from increased sales.
Optimizing Inventory Management
Accurate forecasting and efficient inventory practices are essential. Sellers can:
- Cancel unnecessary shipments.
- Use removal orders to clear slow-moving items.
- Implement inventory management software to predict demand.
Hybrid Fulfillment Strategies
Combining FBA and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) can help manage capacity during peak seasons or with slow-moving inventory. Sellers may also use third-party logistics providers (3PL) to diversify their fulfillment options.
What If You Exceed FBA Capacity Limits
Exceeding capacity limits can lead to several penalties, including:
- Blocked Shipments: Sellers cannot create new shipments when over the limit.
- IPI Score Impact: Persistent overages can lower IPI scores, reducing future capacity.
- Overage Fees: Sellers are charged $10 per cubic foot per month for excess inventory.
- Additional Restrictions: Amazon may impose stricter rules on non-compliant sellers.
Advanced Strategies to Maximize FBA Capacity
To maximize FBA capacity, strategic planning is essential. Sellers should prioritize seasonal forecasting to prepare for peak demand periods, ensuring inventory levels align with anticipated sales.
Utilizing Amazon’s liquidation services can help offload excess stock efficiently, freeing up storage space without incurring penalties. Incorporating collaborative forecasting with suppliers enables synchronized production and inventory management, minimizing overstock risks. Diversifying fulfillment strategies, such as blending FBA with Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) or using third-party logistics providers, offers flexibility during capacity constraints.
By leveraging these advanced strategies, sellers can optimize storage while maintaining smooth operations and maximizing profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why did my FBA capacity limit suddenly decrease?
Capacity limits can change due to a drop in your IPI score, lower sales, or fulfillment center constraints. Regularly monitoring these factors can help maintain consistent limits.
Can I appeal for higher capacity limits?
Yes, you can use the Capacity Manager to request additional space through bidding, but this depends on warehouse availability and your performance metrics.
What tools are available to monitor capacity?
Amazon provides the FBA Capacity Monitor and Capacity Manager within Seller Central to help sellers track and request storage.




